Electrical Contactors vs. Relays: Understanding the Difference
If you work with electrical systems or machinery, you’ve most likely come across the terms contactor and relay. Both of these devices control electrical circuits, but they have different functions and characteristics. How do electrical contactors and relays differ and when should you use one over the other? Knowing their differences and similarities can help you choose the right device for your application.
What Are Electrical Contactors?
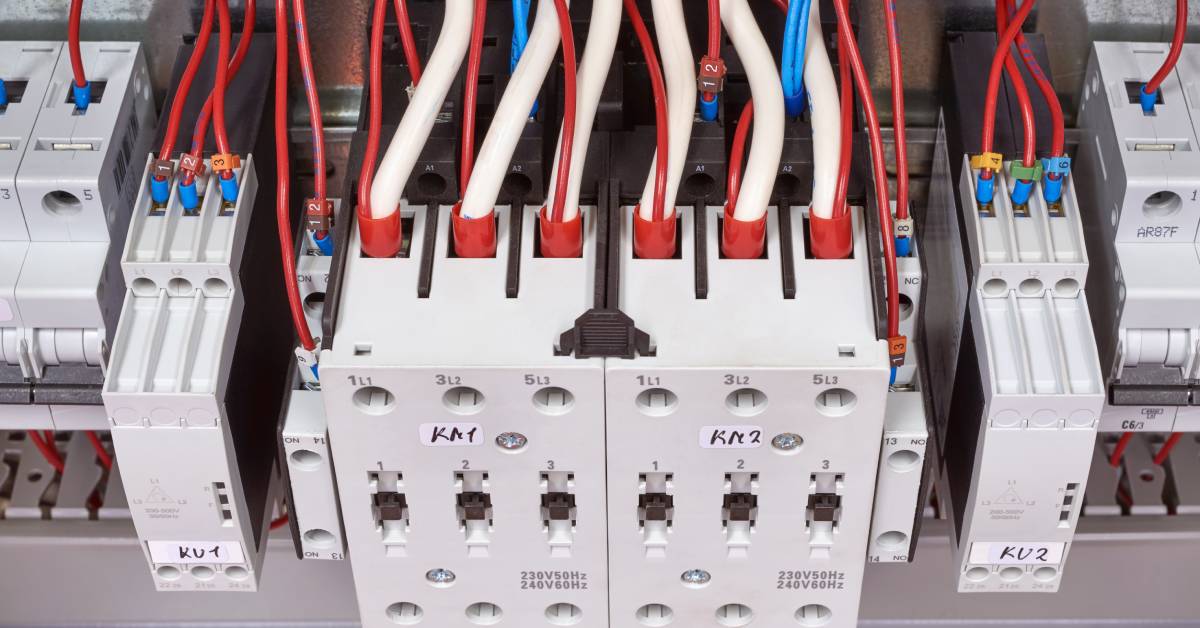
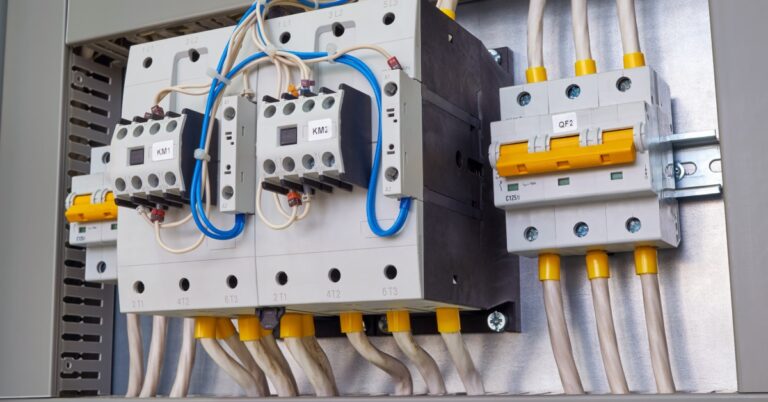
Electrical contactors are electromechanical switches that can handle high currents and voltages. You can think of them as heavy-duty relays. They can handle loads ranging from a few amps to several hundred amps and are commonly used in industrial settings to control high-power devices such as motors, heaters, and lighting systems.
Construction
Contactors consist of three main parts: the coil, contacts, and frame. The coil is an electromagnet that generates a magnetic field when energized. This magnetic field pulls the contacts together, allowing electricity to flow through them. The frame holds these components together and provides protection from external elements.
Applications
Contactors are typically used for controlling electric motors or other high-power loads. They are also commonly found in heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems and lighting control systems.
What Are Relays?
Relays are electronic switches that use a low-power signal to control a high-power circuit. They can handle loads of up to 30 amps and are commonly used in household appliances and automotive applications.
Construction
Relays consist of a coil, armature, and contacts. Energizing the coil creates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, closing the contacts and allowing current to flow through the circuit.
Applications
You can use relays to switch between different power sources, control multiple circuits with one switch, or protect sensitive electronics from high currents.
Differences Between Contactors and Relays
While contactors and relays may have similar functions, there are several differences between them.
- Current and voltage handling: Contactors can handle much higher currents and voltages than relays. This is because they have larger contacts and stronger frames to support the high-power loads they control.
- Construction: Contactors typically have larger physical sizes compared to relays due to their ability to handle higher power levels.
- Application: As mentioned earlier, contactors are commonly used in industrial settings, while relays find more use in household appliances and automotive applications.
When To Use a Contactor or Relay?
So, when should you use a contactor instead of a relay? The answer depends on what you need to control. Here are some guidelines to help you decide:
- Use a contactor when controlling high-power devices, such as motors, in industrial settings.
- Use a relay when controlling low to medium power loads, such as household appliances or automotive systems.
- If the load requires more than 30 amps of current or 240 volts of voltage, use a contactor.
- For lower currents and voltages, a relay will suffice.
While contactors and relays may seem similar at first glance, they serve different purposes in electrical circuits. You can use contactors as heavy-duty switches for controlling high-power loads in industrial settings, while relays act as electronic switches in household appliances and automotive applications. Make sure you know the requirements of your application before choosing between a contactor or relay.
At Tanooga.com, you’ll find high-quality, affordable electrical contactors, which you can use to control your industrial equipment and machinery. We also offer a wide range of relays for various applications. Visit our website to browse our selection.