Contactor or Circuit Breaker? Understanding Their Roles
Electrical systems in commercial and industrial settings require reliable components that manage power safely and efficiently. Two standard devices—contactors and circuit breakers—serve different purposes yet often get compared to one another. Because of this, businesses must understand the roles of contactors and circuit breakers so they can make the right choice and keep their operations safe, efficient, and cost-effective.
What a Contactor Does in Electrical Systems
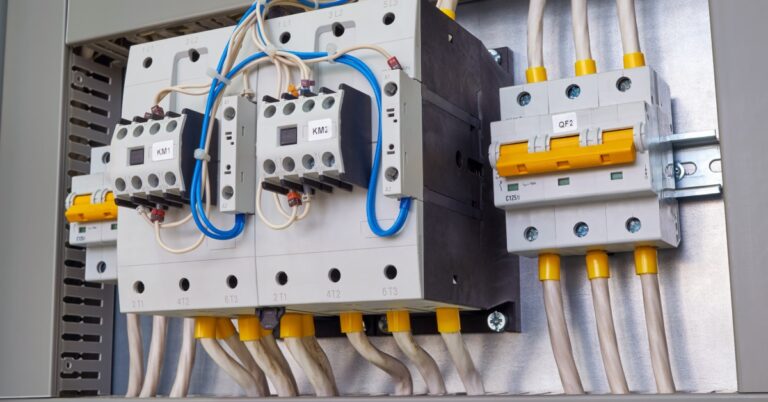
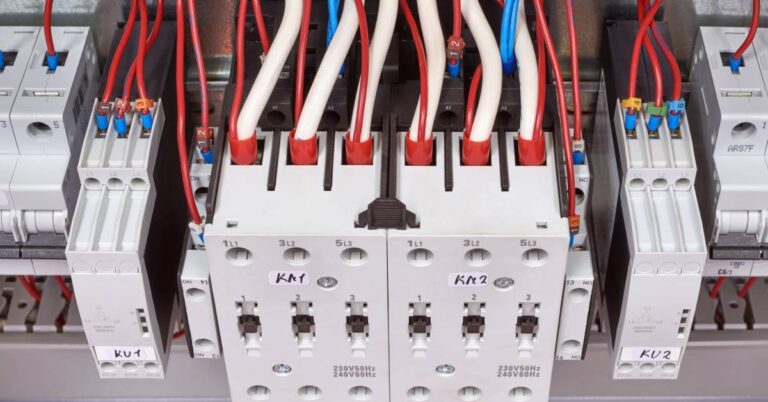
A contactor acts as a switch that controls power flow to equipment. It opens and closes circuits using an electromagnetic coil, allowing operators to manage high-voltage devices with low-voltage control. Contactors switch frequently without damage, making them ideal for use with motors, lighting systems, and heating elements. They also connect easily with overload relays and timers to support advanced automation.
When businesses search for contactors for sale, they look for durability, compatibility with their voltage needs, and ease of installation. Selecting the right size and configuration prevents costly downtime and extends equipment life.
How Circuit Breakers Protect Operations
A circuit breaker acts as a safety device that interrupts power when it detects an overload or short circuit. Unlike a fuse, a breaker resets and restores power once someone clears the issue. Breakers protect against fires, equipment damage, and costly interruptions. They come in various types, including thermal, magnetic, and hybrid designs, each suited to specific applications.
In manufacturing facilities, circuit breakers safeguard heavy machinery, while in offices, they protect essential IT systems. Businesses rely on these components as a frontline defense against electrical hazards, making them a core part of every distribution panel.
Key Differences Between Contactors and Circuit Breakers
While both devices manage power control, their purposes differ. Contactors switch equipment on and off repeatedly during daily operations, while circuit breakers stop current only when a fault occurs. Contactors work best for controlling motors, compressors, or lighting banks, while breakers focus on safety.
Another distinction lies in design. Contactors feature auxiliary contacts for control circuits, whereas breakers emphasize protective mechanisms. When businesses understand this difference, they can prevent improper installation, which can lead to unsafe conditions or equipment failure. Companies that recognize the roles of these devices make more informed choices when expanding facilities or upgrading their electrical infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Business
You can select the correct device by first identifying the application’s purpose. If your goal is to control when equipment powers up and shuts down, a contactor is the proper solution. If you need protection from electrical faults, a circuit breaker delivers it. This essential information helps you better understand the roles of contactors and circuit breakers.
A trusted supplier like The Tanooga Group simplifies the selection process, allowing you to find the right parts for your setup. We offer a variety of brands, sizes, and voltages to fit your specific needs.